Chronic pain is a prevalent and debilitating condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by persistent pain that lasts for more than three to six months, often significantly impacting an individual’s quality of life and placing a substantial economic burden on individuals and healthcare systems. Unlike acute pain, which serves as a warning signal for injury or illness, chronic pain persists even after the initial cause has resolved. It can manifest in various forms, including:
- Burning pain
- Throbbing pain
- Shooting pain
- Aching sensations
The causes of chronic pain are diverse and can include injuries, diseases like arthritis and cancer, nerve damage, and infections . In some cases, the cause of chronic pain remains unknown. It’s important to note that chronic pain can become more complex and challenging to treat over time, emphasizing the need for early intervention and management.
The impact of chronic pain on daily life can be substantial. It can interfere with an individual’s ability to work, perform daily activities, and engage in social interactions. Chronic pain can also lead to:
- Sleep disturbances
- Fatigue
- Mood changes
- Decreased mobility
The emotional and psychological toll of chronic pain can be significant, with many individuals experiencing anxiety, depression, and feelings of isolation.
Peripheral Neuropathy and Chronic Pain
Peripheral neuropathy is a condition that occurs when nerves in the peripheral nervous system are damaged. The peripheral nervous system is responsible for transmitting signals between the brain and spinal cord to the rest of the body. When these nerves are damaged, it can lead to a range of symptoms, including pain, numbness, tingling, and weakness in the affected areas, most commonly the hands and feet.
Peripheral neuropathy can result from various factors, including:
- Diabetes
- Autoimmune diseases
- Infections
- Vitamin deficiencies
- Exposure to toxins
In many cases, the exact cause of peripheral neuropathy remains unknown .
Chronic pain is a frequent symptom of peripheral neuropathy. Research indicates the prevalence of neuropathic pain in various conditions, such as:
| Year | Patients (N°) | Condition | Patients with Neuropathic Pain (N°, %) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | 314 | Diabetic peripheral neuropathy | 115, 37% |
| 2020 | 126 | Diabetic peripheral neuropathy | 53, 42% |
| 2017 | 107 | Brachial plexus injury | 60, 56% |
| 2013 | 86 * | Thoracic surgery | 66% ** |
| 2013 | 106 * | Breast surgery | 68% ** |
| 2013 | 266 * | Hernia surgery | 31% ** |
| 2013 | 142 * | THA/TKA | 6% ** |
| 2008 | 23 | Intercostobrachial neuropathy | 5, 22% |
| 2011 | 12 | Pain after lymph node excision | 10, 83% |
| 2014 | 120 | Chronic, non-malignant pain conditions | 22, 18.3% |
| 2013 | 152 | Neck/upper limb pain | 45, 30% |
| 2012 | 2173 | Any pain condition | 639, 29.4% |
Large epidemiological studies have tested the prevalence of neuropathic pain in diabetic patients. In a cross-sectional study involving 766 diabetic patients, the prevalence of chronic pain with neuropathic characteristics was 20.3%. An observational study was conducted on a wide cohort of diabetic patients receiving community-based healthcare in northwest England (n = 15,692). The prevalence of painful symptoms was 34%, while the prevalence of painful diabetic neuropathy was 21%. The pain can range from mild to severe and may be constant or intermittent. The nature of the pain can vary depending on the type and extent of nerve damage.
Effective Strategies for Managing Chronic Pain in Peripheral Neuropathy
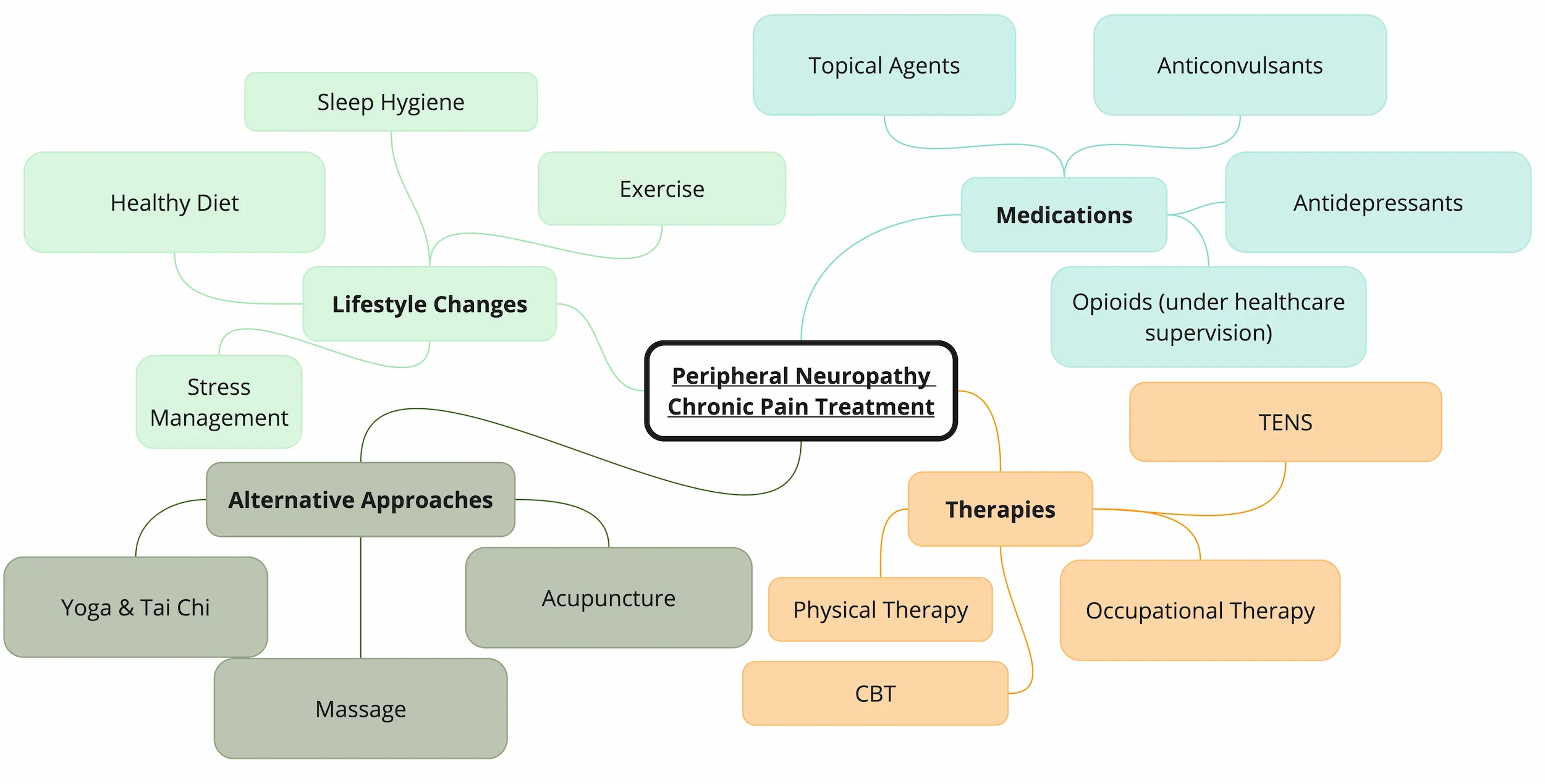
Managing chronic pain in peripheral neuropathy often requires a multimodal approach that combines various strategies to reduce pain intensity, improve functional capacity, and enhance the overall quality of life. It’s crucial to remember that pain experiences and responses to treatment can vary significantly between individuals, highlighting the need for personalized treatment plans.
Medications
Several medications are commonly used to manage chronic pain in peripheral neuropathy. These include:
- Anticonvulsants: Gabapentin and pregabalin are anticonvulsant medications that are often effective in reducing neuropathic pain. They work by modulating the activity of nerve cells involved in pain transmission. Side effects can include dizziness, drowsiness, and gastrointestinal issues.
- Antidepressants: Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs), such as amitriptyline and nortriptyline, and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), such as duloxetine and venlafaxine, can also be helpful in managing neuropathic pain. TCAs affect the levels of norepinephrine and serotonin in the brain, while SNRIs increase the levels of both serotonin and norepinephrine. Side effects of TCAs can include dry mouth, constipation, and drowsiness, while SNRIs may cause nausea, insomnia, and dizziness.
- Topical agents: Lidocaine patches and capsaicin cream can provide localized pain relief. Lidocaine works by numbing the affected area, while capsaicin depletes a chemical called substance P, which is involved in pain transmission. Lidocaine patches may cause skin irritation, while capsaicin cream can cause a burning sensation.
- Opioids: In some cases, opioids may be used to manage severe neuropathic pain when other treatments have not been effective. However, they are typically reserved due to the potential for dependence and side effects such as constipation, nausea, and drowsiness. It’s important to note that even with evidence-based medications, a significant number of patients may not achieve adequate pain relief, emphasizing the need for individualized treatment plans and ongoing monitoring.
Therapies
In addition to medications, various therapies can be beneficial in managing chronic pain in peripheral neuropathy. These include:
- Physical therapy: Physical therapy can help improve strength, flexibility, and range of motion, which can reduce pain and improve functional capacity.
- Occupational therapy: Occupational therapy can help individuals adapt to their daily activities and develop strategies to manage pain while performing tasks.
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT): CBT is a type of psychotherapy that helps individuals identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors that contribute to pain.
- Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS): TENS involves using a device that delivers electrical impulses to the skin to stimulate nerves and reduce pain.
Alternative Approaches
Some individuals with peripheral neuropathy find relief from alternative approaches, such as:
- Acupuncture: Acupuncture involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body to stimulate energy flow and promote healing.
- Massage: Massage can help improve circulation, reduce muscle tension, and promote relaxation, which can alleviate pain . Massage therapy has been shown to enhance blood flow, which helps deliver nutrients and oxygen to affected nerves more efficiently.
- Yoga and tai chi: These mind-body practices combine physical postures, breathing exercises, and meditation to promote relaxation, reduce stress, and improve overall well-being. They can also help reduce stress and improve posture, easing some of the painful effects of neuropathy.
Lifestyle Changes
Certain lifestyle changes can also play a role in managing chronic pain in peripheral neuropathy. These include:
- Exercise: Regular exercise can help improve circulation, reduce stress, and maintain a healthy weight, which can all contribute to pain management . Some beneficial exercises include:
- Walking: Aim for 30 minutes of walking a day, five days a week .
- Low-impact aerobics: Activities like swimming or cycling can improve circulation without putting excessive stress on the joints .
- Resistance training: Strength training can help improve muscle strength and flexibility .
- Stretching: Regular stretching can help increase flexibility and range of motion.
- Diet: A healthy diet that includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help reduce inflammation and provide essential nutrients for nerve health . It’s also important to focus on lean proteins, healthy fats, and fresh, whole foods that fight inflammation.
- Stress management: Stress can exacerbate pain, so it’s essential to incorporate stress-reducing techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, or yoga. Other techniques include:
- Relaxation techniques: These can include progressive muscle relaxation, guided imagery, or listening to calming music.
- Visualization: Close your eyes and imagine a peaceful, restful place or activity. Concentrate on how relaxed this makes you feel.
- Sleep hygiene: Getting adequate sleep is crucial for pain management. Establishing a regular sleep routine, creating a comfortable sleep environment, and addressing sleep disorders can improve sleep quality.
The Role of Mental Health in Managing Chronic Pain
Mental health plays a significant role in managing chronic pain in peripheral neuropathy. Chronic pain can lead to emotional distress, anxiety, and depression, which can further exacerbate pain perception. Addressing mental health concerns is crucial for effective pain management. It’s important to recognize the interconnectedness of physical, psychological, and social factors in chronic pain, highlighting the importance of a holistic approach to treatment.
Psychotherapy, such as CBT, can help individuals develop coping mechanisms for dealing with pain, reduce stress, and improve their overall emotional well-being . Mindfulness-based interventions, such as meditation, can also be helpful in managing pain by promoting relaxation and reducing stress.
Patient Stories and Testimonials
Many individuals with peripheral neuropathy have shared their experiences with managing chronic pain. These stories can provide valuable insights and support for others facing similar challenges.
One patient shared that they experienced severe pain in their feet, which made it difficult to sleep and perform daily activities. After trying various treatments, they found relief through a combination of medication, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes, highlighting the importance of a multimodal approach to pain management.
Another patient described their experience with chronic pain as “walking on fire and ice.” They found that regular exercise, such as walking, helped to reduce their pain and improve their quality of life.
These testimonials highlight the importance of seeking professional help, exploring different treatment options, and finding strategies that work best for each individual.
Prevention
While not all cases of peripheral neuropathy are preventable, certain lifestyle changes can help reduce the risk or delay the onset of the condition. These include:
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Eating a balanced diet
- Exercising regularly
- Avoiding excessive alcohol consumption
- Managing underlying health conditions such as diabetes
Key Takeaway
Chronic pain in peripheral neuropathy is a complex condition that can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. Effective management often requires a multimodal approach that combines medications, therapies, alternative approaches, and lifestyle changes. Addressing mental health concerns is also crucial for successful pain management. By understanding the nature of chronic pain and exploring various treatment options, individuals with peripheral neuropathy can find ways to reduce their pain, improve their functional capacity, and enhance their overall well-being.
It’s important to remember that pain experiences and responses to treatment can vary significantly between individuals, highlighting the need for personalized treatment plans and ongoing monitoring to achieve the best possible outcomes.
Sources:
1. Chronic Pain | Johns Hopkins Medicine, https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/chronic-pain
2. Chronic Pain | Cedars-Sinai, https://www.cedars-sinai.org/health-library/diseases-and-conditions/c/chronic-pain.html
3. Causes of Chronic Pain – Healthline, https://www.healthline.com/health/chronic-pain
4. Long-Term Consequences of Chronic Pain: Mounting Evidence for Pain as a Neurological Disease and Parallels with Other Chronic Disease States | Pain Medicine | Oxford Academic, https://academic.oup.com/painmedicine/article/12/7/996/1840819
5. my.clevelandclinic.org, https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/4798-chronic-pain#:~:text=Unmanaged%20or%20undermanaged%20chronic%20pain,can%20also%20worsen%20chronic%20conditions.
6. Side Effects of Chronic Pain: The Unseen Impact on Your Daily Life, https://southernpainclinic.com/blog/side-effects-of-chronic-pain-the-unseen-impact-on-your-daily-life/
7. Chronic Pain: What It Is, Symptoms, Treatment & Management, https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/4798-chronic-pain
8. Peripheral Neuropathy > Fact Sheets > Yale Medicine, https://www.yalemedicine.org/conditions/peripheral-neuropathy
9. Peripheral Neuropathy | Johns Hopkins Medicine, https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/peripheral-neuropathy
10. Chronic Pain – StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK553030/
11. Acute Pain vs. Chronic Pain: Differences & Causes – Cleveland Clinic, https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/12051-acute-vs-chronic-pain
12. Managing Chronic Neuropathic Pain: Recent Advances and New Challenges – PMC, https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9581623/
13. en.wikipedia.org, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chronic_pain
15. Peripheral neuropathy – Symptoms and causes – Mayo Clinic, https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/peripheral-neuropathy/symptoms-causes/syc-20352061
16. Causes of Peripheral Neuropathy | the Foundation for PN, https://www.foundationforpn.org/causes/
17. Neuropathic Pain Related to Peripheral Neuropathies According to the IASP Grading System Criteria – PubMed Central, https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7821938/
18. Neuropathy: Symptoms & Causes | NewYork-Presbyterian, https://www.nyp.org/neuro/neuromuscular-disorders/neuropathy
19. Quality of Life in Painful Peripheral Neuropathies: A Systematic Review – PMC, https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6556282/
20. A Review of the Emotional Aspects of Neuropathic Pain: From Comorbidity to Co-Pathogenesis – PMC, https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5701895/
21. Pharmacologic management of chronic neuropathic pain: Review of the Canadian Pain Society consensus statement – PMC – PubMed Central, https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5685445/
22. A Comprehensive Algorithm for Management of Neuropathic Pain – PMC – PubMed Central, https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6544553/
23. Medications for Neuropathic Pain | Spine-health, https://www.spine-health.com/treatment/pain-management/medications-neuropathic-pain
24. 10 Treatment Options For Peripheral Neuropathy – Integrated Pain Consultants, https://www.azipc.com/post/10-treatment-options-for-peripheral-neuropathy
25. Treating Painful Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy: An Update | AAFP, https://www.aafp.org/pubs/afp/issues/2016/0801/p227.html
26. www.nhs.uk, https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/peripheral-neuropathy/treatment/
27. Pain-Management Approaches for Peripheral Neuropathy – U.S. Pharmacist, https://www.uspharmacist.com/article/painmanagement-approaches-for-peripheral-neuropathy
28. A Quick Guide to Managing Neuropathy Pain | – Pain and Spine Specialists, https://painandspinespecialists.com/a-quick-guide-to-managing-neuropathy-pain/
29. Types of Neuropathic Pain and Your Treatment Options – Eric K. Fanaee, MD, https://www.drfanaee.com/blog/types-of-neuropathic-pain-and-your-treatment-options
30. Psychologically based interventions for adults with chronic neuropathic pain: a scoping review – Oxford Academic, https://academic.oup.com/painmedicine/article/25/6/400/7600444
31. Treatments for Peripheral Neuropathy | the Foundation for PN, https://www.foundationforpn.org/treatments/
32. Unlocking Relief: Exploring Alternative Therapies for Neuropathy Treatment, https://momentuminjury.com/alternative-therapies-for-neuropathy-treatment/
33. Peripheral neuropathy: 7 natural treatments – MedicalNewsToday, https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/326779
34. Managing Neuropathic Pain: Lifestyle Changes and Coping Strategies – Washington Care Clinic – Mehringer Chiropractic, https://www.mehringerchiropractic.com/managing-neuropathic-pain-lifestyle-changes-and-coping-strategies/
35. lluh.org, https://lluh.org/services/neuropathic-therapy-center/blog/4-exercises-reduce-chronic-nerve-pain
36. Managing Peripheral Neuropathy | Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, https://www.mskcc.org/cancer-care/patient-education/managing-peripheral-neuropathy
37. Solved! Foods To Avoid If You Have Neuropathy! – Chiropractor New Berlin WI, https://www.chiropractornewberlin.com/foods-to-avoid-with-neuropathy/
38. Five Lifestyle Changes for Peripheral Neuropathy – WinSanTor, https://winsantor.com/five-lifestyle-changes-to-relieve-symptoms-for-peripheral-neuropathy/
39. Management & Care | the Foundation for Peripheral Neuropathy, https://www.foundationforpn.org/living-well/lifestyle/managing-peripheral-neuropathy/
40. Peripheral Neuropathy and Mental Health, https://www.foundationforpn.org/peripheral-neuropathy-and-mental-health/
41. Peripheral Neuropathy Patient Testimonials – Smith Chiropractic, https://www.smithchirocos.com/testimonials/peripheral-neuropathy-142. Neuropathy Testimonials – Nerve and Muscle Center of Texas, https://www.nerveandmuscle.org/neuropathy-testimonials/