Alcoholic neuropathy, also known as alcohol-related neuropathy, is a type of peripheral neuropathy resulting from excessive and prolonged alcohol consumption. This condition arises when the peripheral nerves, responsible for transmitting signals between the brain and spinal cord to the rest of the body, are damaged1. Alcoholism, now called alcohol use disorder (AUD), is a condition in which you have difficulty stopping or managing your alcohol intake despite experiencing negative consequences. According to the National Institutes of Health, nearly 29 million people had AUD in the United States in 20212. Over time, the effects of drinking too much alcohol may cause alcoholic neuropathy. This comprehensive guide delves into the causes, diagnosis, and treatment of alcoholic neuropathy, offering insights into this often-overlooked consequence of alcohol abuse.
Watch the detailed podcast discussion aboutalcoholic peripheral neuropathy
Causes of Alcoholic Neuropathy
While the exact cause of alcoholic neuropathy is unknown, it likely involves a combination of direct nerve poisoning by alcohol and the effects of poor nutrition3. Several factors contribute to its development:
- Direct Toxicity of Alcohol: Alcohol and its metabolites, such as acetaldehyde, have direct toxic effects on nerve tissues4. These substances can disrupt nerve function and structure, leading to impaired signal transmission and nerve damage.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Chronic alcohol abuse often leads to malnutrition and deficiencies in essential nutrients, particularly B vitamins like thiamine (vitamin B1)4. These vitamins play a crucial role in maintaining nerve health, and their deficiency can exacerbate nerve damage caused by alcohol1. Alcohol can interfere with the body’s ability to absorb, process, and utilize these essential nutrients, further contributing to the development of alcoholic neuropathy3.
- Impact on Organ Function: Alcohol also alters the function of the stomach, liver, and kidneys, preventing the body from properly detoxifying waste materials. This waste buildup can harm many regions of the body, including the nerves5.
- Genetic Predisposition: Some individuals may have a genetic predisposition that makes them more susceptible to alcohol-related nerve damage4.
- Overall Health and Lifestyle Factors: Overall physical health, liver function, and the concurrent use of other substances can also influence the onset and severity of alcoholic neuropathy4.
How Much Alcohol Consumption Leads to Alcoholic Neuropathy?
The amount of alcohol consumption that can lead to alcoholic neuropathy varies depending on individual factors such as genetics, overall health, and nutritional status. However, studies indicate that consuming more than 100 grams of alcohol per day over many years significantly increases the risk of developing peripheral neuropathy6. It’s important to note that even moderate alcohol consumption over an extended period can contribute to nerve damage in some individuals.
Symptoms of Alcoholic Neuropathy
Alcoholic neuropathy typically begins with subtle symptoms that gradually worsen over time. However, heavy binge drinking can accelerate the onset of symptoms7. These symptoms often affect the extremities first, particularly the feet and hands. The effects of alcoholic neuropathy fall into four main categories: decreased sensation, pain/hypersensitivity, muscle weakness, and autonomic effects5.
- Tingling or Numbness: A sensation of “pins and needles” or a loss of feeling in the hands and feet.
- Burning Pain: Intense burning sensations in the affected areas.
- Hyperalgesia: Increased sensitivity to pain.
- Allodynia: A condition in which normal stimuli, like a soft touch, produce pain.
Motor Symptoms:
- Muscle Weakness: Difficulty with movements requiring fine motor skills, such as buttoning clothes or writing.
- Muscle Cramps: Involuntary muscle contractions that can be painful.
- Loss of Coordination: Difficulty with balance and coordination, leading to an increased risk of falls.
Autonomic Symptoms:
- In advanced cases, alcoholic neuropathy can affect the autonomic nervous system, leading to problems with blood pressure regulation, digestion, and bladder control.
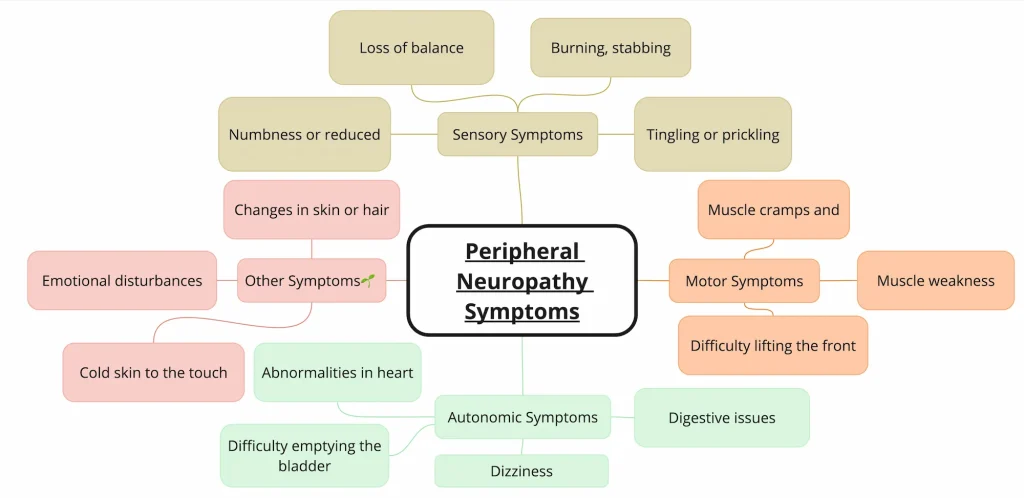
The symptoms of alcoholic neuropathy can significantly impair an individual’s quality of life4.
Diagnosing Alcoholic Neuropathy
Diagnosing alcoholic neuropathy involves a comprehensive evaluation that considers the individual’s medical history, physical examination, and various diagnostic tests.
Self-Assessment
While there are no specific self-diagnosis methods for alcoholic neuropathy, individuals experiencing symptoms suggestive of the condition should seek medical attention. Recognizing the symptoms and understanding the potential link to alcohol consumption is crucial for early intervention.
Doctor Tests
Doctors employ several tests to diagnose alcoholic neuropathy and rule out other possible causes of neuropathy, such as diabetes, vitamin deficiencies, and HIV. These tests may include:
- Blood Tests: To assess overall health, liver function, and nutritional status, including vitamin B levels8. Doctors may check for a deficiency (lack) of:
- Thiamine (vitamin B1)
- Pyridoxine (vitamin B6)
- Vitamin B12
- Folic acid 9
- Nerve Conduction Studies: To measure the speed and strength of nerve signals, helping to identify the extent of nerve damage1.
- Electromyography (EMG): To evaluate the electrical activity of muscles, providing insights into the health of nerves and muscles9. EMG and NCV tests examine nerve function in detail. Characteristic patterns, such as decreased function in the hands and feet, low amplitude of nerve waves, and slowing of nerve function, are suggestive of alcoholic neuropathy5.
- Nerve Biopsy: In some cases, a small sample of nerve tissue may be taken for examination under a microscope to assess nerve damage1.
Treatment of Alcoholic Neuropathy
The primary treatment for alcoholic neuropathy is to stop or significantly reduce alcohol consumption. This often requires professional help, such as inpatient or outpatient rehabilitation, medication, support groups, and psychotherapy1. While abstaining from alcohol can help improve symptoms and prevent further damage, some alcohol-induced nerve damage may be permanent2.
Once alcohol consumption is addressed, treatment focuses on managing the symptoms and preventing further nerve damage. This may involve:
- Vitamin Supplements: Replenishing essential nutrients, particularly B vitamins, can help improve nerve function and alleviate symptoms1. It is important to supplement the diet with vitamins, including thiamine and folic acid3.
- Pain Relief Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers or prescription medications may be used to manage pain and discomfort1.
- Physical Therapy: Gentle exercises and activities can help improve muscle strength, balance, and coordination1. Physical therapy and orthopedic appliances (such as splints) may be needed to maintain muscle function and limb position3.
- Mobility Aids: Assistive devices such as canes, walkers, or braces may be necessary to improve mobility and prevent falls1.
- Alternative Therapies: Some individuals may find relief from alternative therapies such as acupuncture or herbal remedies2.
- Treating Other Conditions: If there are other medical problems that can also cause nerve damage, such as diabetes, they should be treated as well3.
Supplements for Alcoholic Neuropathy
For an indepth guide about peripheral neuropathy supplements and vitamins, read this article.
| Supplement | Description | Potential Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| B Vitamins | Essential for nerve function, especially B1 (thiamine), B6, and B12 | Can help address deficiencies and support nerve regeneration 10 |
| Alpha-Lipoic Acid | Antioxidant | May help protect nerves from damage and improve nerve function 11 |
| Acetyl-L-Carnitine | Amino acid | May help improve nerve cell health and reduce pain 11 |
| Curcumin | Compound found in turmeric with anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties | May benefit nerve health 11 |
| Fish Oil | Contains omega-3 fatty acids with anti-inflammatory effects | May support nerve repair 10 |
While many supplements exist for neuropathy, research supporting their use is not always well-established12. It’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional before taking any supplements, as they can interact with medications or have potential side effects.
Clinical Trials Related to Alcoholic Neuropathy Treatments
Several clinical trials have investigated various aspects of alcoholic neuropathy and its treatment. Here are some notable examples:
- Thiamine Status in Alcoholic Neuropathy: A study by Michalak et al. investigated thiamine status in patients with alcoholic neuropathy compared to those with diabetic neuropathy. The findings suggested that while erythrocyte transketolase activity, an indicator of thiamine status, was decreased in both groups, there was no significant difference in thiamine pyrophosphate levels between the two groups13.
- Gender Differences in Alcoholic Neuropathy: A study by Ammendola and colleagues explored gender differences in the development of alcoholic neuropathy. The research indicated that women with chronic alcoholism might be more susceptible to developing neuropathy, as evidenced by lower sural sensory nerve action potential (SNAP) amplitude, even after controlling for nutritional deficiencies13.
- Effectiveness of Vitamin B Complex: A multi-center, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study evaluated the efficacy of a specific vitamin B complex in treating alcoholic polyneuropathy. The results showed that the vitamin B complex, with and without folic acid, significantly improved sensory symptoms over a 12-week treatment period14.
- Prevalence of Peripheral Neuropathy in Chronic Alcohol Abusers: A review of 41 studies investigated the prevalence of peripheral neuropathy in chronic alcohol abusers. The pooled prevalence of peripheral neuropathy diagnosed using history, examination, and/or electrophysiology was found to be 44.2%15.
These clinical trials provide valuable insights into the diagnosis, treatment, and prevalence of alcoholic neuropathy.
Support Groups and Resources for People with Alcoholic Neuropathy
Several support groups and resources are available to help individuals with alcoholic neuropathy and their families. These resources can provide valuable information, support, and coping strategies.
- The Western Neuropathy Association (WNA): Offers support groups and resources for patients in California, Nevada, and Oregon. Their website is www.pnhelp.org16.
- The Foundation for Peripheral Neuropathy: Provides support groups and resources for patients in other states. Their website is www.foundationforpn.org, and their phone number is (877) 883-994216.
These organizations can help connect individuals with support groups, educational materials, and healthcare professionals specializing in neuropathy.
Case Studies and Anecdotes
While the research material provided does not include detailed anecdotes of individuals cured of alcoholic neuropathy, it does offer some insights into the recovery process.
One study examined the effectiveness of a specific vitamin B complex in treating alcoholic polyneuropathy. The results showed that the vitamin B complex significantly improved symptoms over a 12-week treatment period14. This highlights the importance of addressing nutritional deficiencies in the recovery process.
Another study investigated the prevalence of autonomic and peripheral neuropathy among patients with alcoholism. The findings indicated that these types of neuropathy are common among alcoholics and that alcohol has a dose-dependent toxic effect on both autonomic and peripheral nerves17. This emphasizes the need for early intervention and alcohol cessation to prevent further nerve damage.
Conclusion
Alcoholic neuropathy is a severe consequence of excessive and prolonged alcohol consumption. The damage to the peripheral nerves can lead to a range of debilitating symptoms that significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. While the nerve damage may be irreversible in some cases, early diagnosis and intervention can help manage symptoms, prevent further damage, and improve overall health. The key to recovery lies in addressing alcohol consumption, correcting nutritional deficiencies, and adopting a healthy lifestyle. This research highlights the complex interplay of factors contributing to alcoholic neuropathy, the importance of early diagnosis and treatment, and the potential for recovery with appropriate interventions.
Scientific Sources
1. Alcoholic neuropathy: Causes, symptoms, and treatment , https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/321858
2. Alcoholic Neuropathy: Causes, Symptoms, and Diagnosis – Healthline , https://www.healthline.com/health/alcoholism/alcoholic-neuropathy
3. Alcoholic neuropathy Information | Mount Sinai – New York , https://www.mountsinai.org/health-library/diseases-conditions/alcoholic-neuropathy
4. How Long Does Alcoholic Neuropathy Take to Go Away? – Resurgence Behavioral Health , https://resurgencebehavioralhealth.com/blog/how-long-does-alcoholic-neuropathy-take-to-go-away/
5. Alcoholic Neuropathy: Causes, Symptoms, & Treatments , https://www.verywellmind.com/understanding-alcoholic-neuropathy-4142252
6. Alcoholic Neuropathy – StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf , https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK499856/
7. How Much Alcohol Consumption Causes Neuropathy? – Fox Integrated Healthcare , https://foxintegratedhealthcare.com/neuropathy/how-much-alcohol-consumption-causes-neuropathy/
8. Alcoholic Neuropathy: Symptoms, Diagnosis, & Outlook | Rehabs.com , https://rehabs.com/alcohol/effects/neuropathy/
9. medlineplus.gov , https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000714.htm
10. Supplements for Neuropathy: Vitamins and More – Healthline , https://www.healthline.com/health/neuropathy-supplements
11. pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov , https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3370340/#:~:text=Benfotiamine%2C%20alpha%2Dlipoic%20acid%2C,N%2Dacetylcysteine%20and%20topical%20capsaicin.
12. Supplements for Neuropathy: Do They Work? – Verywell Health , https://www.verywellhealth.com/supplements-for-neuropathy-8550168
13. Alcoholic Neuropathy: Practice Essentials, Pathophysiology, Epidemiology , https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/315159-overview
14. TREATMENT OF ALCOHOLIC POLYNEUROPATHY WITH VITAMIN B COMPLEX: A RANDOMISED CONTROLLED TRIAL – Oxford Academic , https://academic.oup.com/alcalc/article/41/6/636/157556
15. Alcohol-related peripheral neuropathy: a systematic review and meta-analysis – PMC , https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6851213/
16. Find A Support Group – Neuropathy Action Foundation , http://www.neuropathyaction.org/neuropathy_101/find_a_support_group.htm
17. I drank too much and now I can’t walk: a case of alcohol-induced dysautonomia – PMC , https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8366070/
