Peripheral neuropathy, a condition arising from damage to the peripheral nervous system, affects millions of individuals. This intricate network of nerves relays signals between the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) and the rest of the body. When these nerves are damaged, it can lead to a range of symptoms, including pain, numbness, tingling, and muscle weakness in the extremities1. Nerve studies play a crucial role in diagnosing peripheral neuropathy, helping healthcare providers determine the underlying cause and guide treatment decisions. This article delves into the different types of nerve studies, their procedures, benefits, potential problems, and alternative diagnostic methods.
Understanding Peripheral Neuropathy
Neuropathy refers to damage or disease affecting the nerves, which can impair sensation, movement, gland or organ function2. Peripheral neuropathy is a disorder that occurs when nerves of the peripheral nervous system are damaged. This damage disrupts the nerves’ ability to communicate effectively with the brain, skin, and muscles3. The peripheral nervous system encompasses all the nerves outside the brain and spinal cord4. When these nerves are damaged, they may not be able to send or receive messages properly, leading to issues with sensation, strength, and coordination in various body parts, particularly the extremities3. Peripheral neuropathy can stem from various factors, including diabetes-related complications, autoimmune diseases, vitamin deficiencies, infections, and genetic conditions3.
The peripheral nervous system includes motor nerves responsible for movement, sensory nerves that transmit sensations like touch and temperature, and autonomic nerves that control involuntary functions like breathing and heart rate. Peripheral neuropathy can affect one or more of these nerve types, leading to a variety of symptoms1.
Common Symptoms of Peripheral Neuropathy
The symptoms of peripheral neuropathy can vary depending on the type of nerves affected and the extent of the damage. Some common symptoms include: 7
- Numbness and tingling in the hands and feet
- Burning, stabbing, or shooting pain in the affected areas
- Loss of balance and coordination
- Muscle weakness, especially in the feet
- Gradual onset of numbness, prickling, or tingling in your feet or hands, which can spread upward into your legs and arms
- Sharp, jabbing, throbbing, or burning pain
- Extreme sensitivity to touch
- Pain during activities that shouldn’t cause pain, such as pain in your feet when putting weight on them or when they’re under a blanket
In addition to these physical symptoms, peripheral neuropathy can also cause muscle weakness and atrophy (shrinking) due to nerve damage4. In some cases, it can also lead to uncontrolled muscle movements, such as twitching or spasms4. Furthermore, peripheral neuropathy can lead to emotional disturbances, such as anxiety and depression, and sleep disruptions due to pain or discomfort6.
It’s crucial to seek immediate medical attention if you experience sudden numbness or weakness, especially on one side of the body, as this could indicate a stroke. Similarly, rapidly progressing muscle weakness that starts in the feet and moves upward could be a sign of Guillain-Barré syndrome, a serious condition requiring urgent treatment4.
Nerve Studies: An Overview
Nerve studies, also known as nerve conduction studies (NCS) and electromyography (EMG), are diagnostic tests that evaluate the function of nerves and muscles10. These tests help healthcare providers assess how well the nerves transmit electrical signals and how the muscles respond to those signals10. By analyzing the electrical activity of nerves and muscles, nerve studies can help identify nerve damage, pinpoint the location of the damage, and determine the severity of the condition11.

Types of Nerve Studies
There are two main types of nerve studies used to diagnose peripheral neuropathy:
- Nerve Conduction Studies (NCS): NCS measure how fast and how well electrical signals travel along nerves13. During the test, electrodes are placed on the skin over the nerve being tested13. A small electrical impulse is delivered to the nerve, and the speed and strength of the nerve signal are measured15. This helps determine if there is any blockage or damage to the nerve pathway16.
- Electromyography (EMG): EMG assesses the electrical activity of muscles17. A thin needle electrode is inserted into the muscle, and the electrical activity is recorded both at rest and during contraction18. This helps determine if there is any muscle damage or if the muscle is receiving proper signals from the nerves19.
How Nerve Studies are Conducted
Preparation for Nerve Studies
Before undergoing nerve studies, patients are typically advised to:
- Bathe or shower on the day of the test to remove body oils and lotions20.
- Avoid using lotions, creams, or perfumes on the skin15.
- Wear comfortable, loose-fitting clothing20.
- Inform the healthcare provider about any medical conditions, such as bleeding disorders or pacemakers15.
- Eat normally and take medications as usual, unless otherwise instructed21.
Nerve Conduction Study Procedure
During an NCS:
- Electrodes are placed on the skin over the nerve being tested16.
- A small electrical impulse is delivered to the nerve through a stimulating electrode22.
- The response is recorded by another electrode placed over the muscle supplied by that nerve16.
- The speed and strength of the nerve signal are measured14.
- The process may be repeated in several areas of the body16.
Electromyography Procedure
During an EMG:
- A thin needle electrode is inserted into the muscle being tested23.
- The electrical activity of the muscle is recorded at rest and during contraction23.
- The patient may be asked to contract the muscle slightly and then forcefully23.
- The electrical activity is displayed on a monitor and may also be heard through an audio speaker14.
Interpretation of Nerve Study Results
Neurologists interpret the results by analyzing the speed of nerve signals (NCV), the strength of the signals (amplitude), and the time it takes for signals to travel (latency)24. These factors, along with your symptoms, help determine if your nerves are damaged and where the damage might be25.
Potential Problems and Benefits of Nerve Studies
Problems with Nerve Studies
While nerve studies are generally safe and well-tolerated, there are some potential problems to consider:
- Discomfort: Some patients may experience mild discomfort or pain during the NCS due to the electrical stimulation26.
- Bleeding or Bruising: There is a small risk of bleeding or bruising at the needle insertion site during EMG27.
- Infection: Although rare, there is a slight risk of infection at the needle insertion site27.
- Inaccurate Results: Certain factors, such as cold body temperature or damage to the spinal cord, can interfere with the accuracy of nerve study results22.
Benefits of Nerve Studies
Despite these potential drawbacks, nerve studies offer significant benefits in diagnosing peripheral neuropathy:
- Accurate Diagnosis: Nerve studies can help confirm the presence of peripheral neuropathy and differentiate it from other conditions with similar symptoms29.
- Localization of Damage: Nerve studies can pinpoint the location of nerve damage, which is crucial for determining the underlying cause and guiding treatment15.
- Assessment of Severity: Nerve studies can help assess the severity of nerve damage, which can influence treatment decisions and prognosis15.
- Monitoring Disease Progression: Nerve studies can be used to monitor the progression of peripheral neuropathy over time and evaluate the effectiveness of treatment29.
Accuracy of Nerve Studies
While nerve conduction studies are not always definitive, they have shown high diagnostic accuracy for certain conditions, such as carpal tunnel syndrome, with sensitivities around 85% and specificities around 97%30. However, it’s important to note that nerve studies are not always definitive, and the results should be interpreted in conjunction with other clinical findings31.
Risks and Side Effects of Nerve Studies
The risks associated with nerve studies are generally low. The electrical stimulation used in NCS is very mild and does not cause any long-term side effects22. The main side effect is short-term discomfort from the electrical impulses22. In EMG, the most common side effect is mild soreness in the tested muscles for a few days after the test14.
Alternative Diagnostic Methods for Peripheral Neuropathy
In addition to nerve studies, healthcare providers may use other diagnostic methods to evaluate peripheral neuropathy, including:
- Blood tests: These can detect underlying conditions that may be causing peripheral neuropathy, such as diabetes, vitamin deficiencies, and autoimmune disorders32.
- Imaging tests: CT or MRI scans can help identify structural abnormalities that may be compressing or damaging nerves, such as herniated disks or tumors32.
- Nerve biopsy: In some cases, a small sample of a nerve may be removed and examined under a microscope to identify the cause of the neuropathy32.
- Skin biopsy: This involves removing a small sample of skin to analyze nerve fibers and assess small fiber neuropathy32.
- Quantitative sensory testing: This assesses the function of sensory nerves by measuring the perception of different stimuli, such as vibration, temperature, and pain32.
- Autonomic reflex screen: This evaluates the function of autonomic nerves, which control involuntary bodily functions like heart rate and blood pressure32.
Comparing Alternative Diagnostic Methods with Nerve Studies
It’s important to recognize that nerve studies are often used in conjunction with other diagnostic methods, such as blood tests and imaging studies, to provide a comprehensive evaluation of peripheral neuropathy32. Each method offers unique insights, and their combined use can lead to a more accurate diagnosis and treatment plan32.
While imaging techniques like MRI excel at visualizing structural abnormalities, nerve studies provide a more direct assessment of nerve function35. Ultrasound can be a valuable alternative for certain types of neuropathy, offering advantages in terms of patient comfort and cost-effectiveness, but it may not be as accurate as nerve studies in all cases36.
Early diagnosis of peripheral neuropathy is crucial, as it allows for timely intervention and may help prevent further nerve damage and disability. Nerve studies play a vital role in early detection, especially in individuals with risk factors for neuropathy, such as diabetes37.
Cost and Insurance Coverage of Nerve Studies
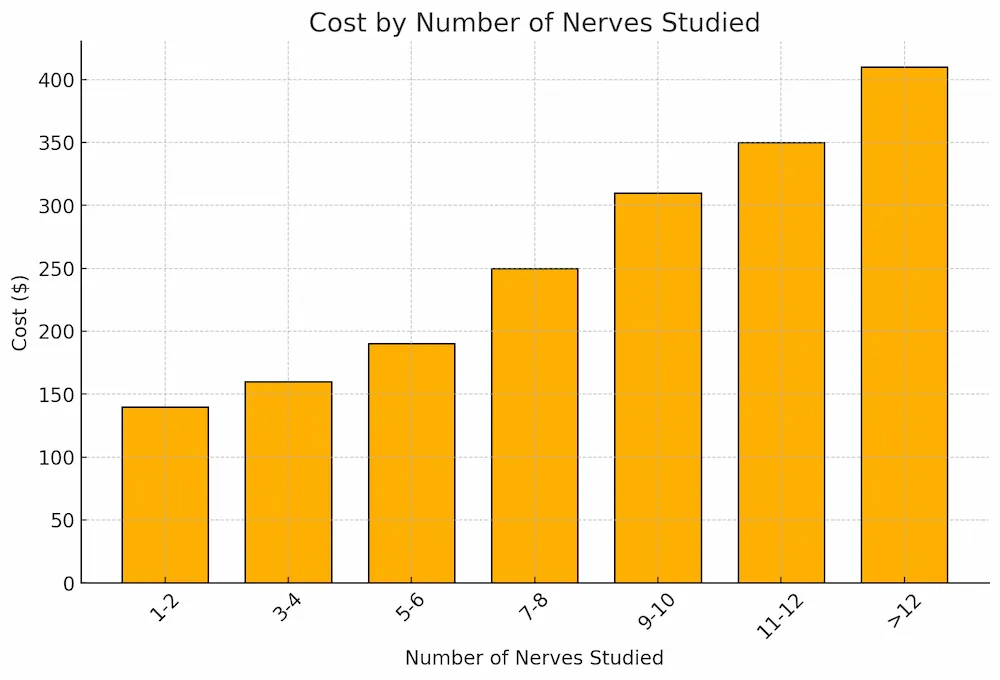
The cost of nerve studies can vary depending on the number of nerves tested, the complexity of the study, and the location of the testing facility38. Some typical costs for nerve conduction studies are: 39
| Number of Nerves Studied | Cost |
|---|---|
| 1-2 | $140 |
| 3-4 | $160 |
| 5-6 | $190 |
| 7-8 | $250 |
| 9-10 | $310 |
| 11-12 | $350 |
| >12 | $410 |
Insurance coverage for nerve studies varies depending on the insurance plan and the medical necessity of the test40. In general, insurance plans are more likely to cover nerve studies when they are used to diagnose a specific condition or guide treatment decisions41. Insurance coverage for nerve conduction studies can vary depending on the type of study and the device used. Some insurance plans may not cover automated point-of-care nerve conduction studies using portable hand-held devices42. It’s essential to check with the insurance provider to determine coverage and any pre-authorization requirements.
Key Takeaway
In conclusion, nerve studies are essential tools for diagnosing and managing peripheral neuropathy. They provide a detailed assessment of nerve function, enabling healthcare providers to identify the presence, location, and extent of nerve damage. This information is crucial for determining the underlying cause of neuropathy, guiding treatment decisions, and monitoring disease progression.
While alternative diagnostic methods exist, nerve studies offer unique advantages in terms of accuracy and direct assessment of nerve function. By understanding the role and value of nerve studies, patients and healthcare providers can work together to effectively address peripheral neuropathy and improve patient outcomes.
Sources Used
1. Peripheral Neuropathy | National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, https://www.ninds.nih.gov/health-information/disorders/peripheral-neuropathy
2. en.wikipedia.org, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Peripheral_neuropathy
3. Peripheral Neuropathy > Fact Sheets > Yale Medicine, https://www.yalemedicine.org/conditions/peripheral-neuropathy
4. Peripheral Neuropathy: What It Is, Symptoms & Treatment – Cleveland Clinic, https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/14737-peripheral-neuropathy
5. Peripheral neuropathy: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia, https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000593.htm
6. Peripheral Neuropathy | Johns Hopkins Medicine, https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/peripheral-neuropathy
8. Peripheral neuropathy – Symptoms and causes – Mayo Clinic, https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/peripheral-neuropathy/symptoms-causes/syc-20352061
9. Peripheral neuropathy – NHS, https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/peripheral-neuropathy/
11. Nerve conduction study – Wikipedia, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nerve_conduction_study
12. Nerve Conduction Studies McKinney | Electromyogram Frisco, Plano, Allen, https://www.dallaspaindoc.com/nerve-conduction-studies-ncs-pain-management-physician-mckinney.html
13. www.hopkinsmedicine.org, https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/treatment-tests-and-therapies/nerve-conduction-studies#:~:text=A%20nerve%20conduction%20velocity%20(NCV,patches%20put%20on%20your%20skin.
14. Electromyography (EMG) and Nerve Conduction Studies: MedlinePlus Medical Test, https://medlineplus.gov/lab-tests/electromyography-emg-and-nerve-conduction-studies/
15. Nerve Conduction Study: What It Is, Procedure & Results, https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/treatments/24821-nerve-conduction-study
16. Spinal Diagnostics: Nerve Conduction Studies | Cedars-Sinai, https://www.cedars-sinai.org/health-library/diseases-and-conditions/s/spinal-diagnostics-nerve-conduction-studies.html
17. www.hopkinsmedicine.org, https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/treatment-tests-and-therapies/electromyography-emg#:~:text=Electromyography%20(EMG)%20measures%20muscle%20response,to%20help%20detect%20neuromuscular%20abnormalities.
18. Electromyography (EMG) | Johns Hopkins Medicine, https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/treatment-tests-and-therapies/electromyography-emg
19. Electromyography – Wikipedia, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electromyography
20. Prepare for Your EMG and Nerve Conduction Studies – Noran Neurological Clinic, https://www.noranclinic.com/services/emgncs/prepare-your-emg-and-nerve-conduction-studies
21. Nerve Conduction Study Instructions for Patients – Houston, TX – The Endocrine Center, https://www.endocrinecenter.com/contents/educational-information/nerve-conduction-study-instructions-for-patients
22. Nerve Conduction Studies | Johns Hopkins Medicine, https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/treatment-tests-and-therapies/nerve-conduction-studies
23. EMG (Electromyography): What It Is, Purpose, Procedure & Results – Cleveland Clinic, https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diagnostics/4825-emg-electromyography
24. Interpretation of electrodiagnostic studies – how to apply it to the practice of orthopaedic surgery – PMC, https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8217100/
25. Deciphering EMG Results: Unraveling the Secrets of Nerve and Muscle Function – Island Rheumatology, https://islandrheumatology.com/deciphering-emg-results/
26. Potential risks of iatrogenic complications of nerve conduction studies (NCS) and electromyography (EMG) – PMC, https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6123846/
27. Electromyography (EMG) & Nerve Conduction Studies – Mayfield Brain & Spine, https://mayfieldclinic.com/pe-emg.htm
28. www.hopkinsmedicine.org, https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/treatment-tests-and-therapies/nerve-conduction-studies#:~:text=Risks%20depend%20on%20your%20specific,the%20test%2C%20and%20body%20temperature.
29. Nerve conduction studies: understanding the role. – Lone Star Neurology, https://lonestarneurology.net/blog/nerve-conduction-studies/
30. Using and interpreting electrodiagnostic tests | Cleveland Clinic Journal of Medicine, https://www.ccjm.org/content/87/11/671
31. Accuracy of in-office nerve conduction studies for median neuropathy: a meta-analysis, https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21131139/
32. Peripheral neuropathy – Diagnosis and treatment – Mayo Clinic, https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/peripheral-neuropathy/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20352067
33. Diagnosing Peripheral Neuropathy | NYU Langone Health, https://nyulangone.org/conditions/peripheral-neuropathy/diagnosis
34. Diagnostic value of ultrasonography versus electrodiagnosis in ulnar neuropathy, https://www.dovepress.com/diagnostic-value-of-ultrasonography-versus-electrodiagnosis-in-ulnar-n-peer-reviewed-fulltext-article-MDER
35. Nerve Conduction Studies vs. Imaging Techniques: When to Choose What?, https://www.sprintdiagnostics.in/blog/nerve-conduction-studies-vs-imaging-techniques
36. A Comparative Analysis Between Ultrasound and Electromyographic and Nerve Conduction Studies in Diagnosing Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS), https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9674040/
37. Comparison of Automated versus Traditional Nerve Conduction Study Methods for Median Nerve Testing in a General Worker Population – CDC stacks, https://stacks.cdc.gov/view/cdc/31008
38. How Much Does a Nerve Conduction Studies 7-8 Nerves Cost Near Me? – MDsave, https://www.mdsave.com/procedures/nerve-conduction-studies-7-8-nerves/d786fec4
39. Our Pricing – PA Physical Medicine, https://www.paphysicalmedicine.com/our-pricing/
40. Nerve Conduction Studies Technologist Malpractice Insurance – CM&F Group, https://www.cmfgroup.com/malpractice-insurance/cardiology-respiratory-neurology-professionals/nerve-conduction-studies-technologist-malpractice-insurance/
41. Nerve Conduction Studies – Medical Clinical Policy Bulletins | Aetna, https://www.aetna.com/cpb/medical/data/500_599/0502.html42. Medical Coverage Policy Nerve Velocity Conduction Studies, EMGs, Points of Care Nerve Conduction Tests – Blue Cross Blue Shield of Rhode Island, https://www.bcbsri.com/sites/default/files/polices/NerveConductionVelocityStudies&EMGs_0.pdf

